IQuS Publications
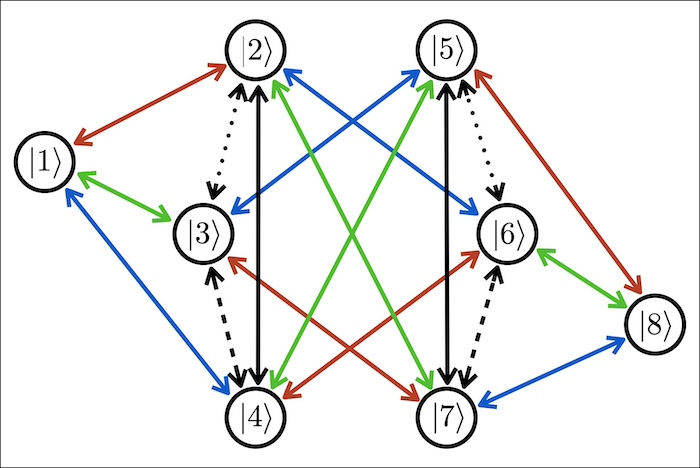
Qu8its for Quantum Simulations of Lattice Quantum Chromodynamics
We explore the utility of d=8 qudits, qu8its, for quantum simulations of the dynamics of 1+1D SU(3) lattice quantum chromodynamics, including a mapping for arbitrary numbers of flavors and lattice size and a re-organization of the Hamiltonian for efficient time-evolution. Recent advances in parallel gate applications, along with the shorter application times of single-qudit operations compared with two-qudit operations, lead to significant projected advantages in quantum simulation fidelities and circuit depths using qu8its rather than qubits. The number of two-qudit entangling gates required for time evolution using qu8its is found to be more than a factor of five fewer than for qubits. We anticipate that the developments presented in this work will enable improved quantum simulations to be performed using emerging quantum hardware.
This work was supported, in part, by Universität Bielefeld and ERC-885281-KILONOVA Advanced Grant (Caroline Robin), by U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics, Inqubator for Quantum Simulation (IQuS)9 under Award Number DOE (NP) Award DE-SC0020970 (Martin Savage), and the Quantum Science Center (QSC), a National Quantum Information Science Research Center of the U.S. Department of Energy (Marc Illa). This work was supported, in part, through the Department of Physics and the College of Arts and Sciences at the University of Washington.
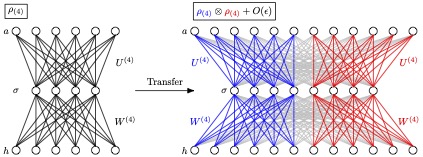
Real-time Dynamics of the Schwinger Model as an Open Quantum System with Neural Density Operators
Ab-initio simulations of multiple heavy quarks propagating in a Quark-Gluon Plasma are computationally difficult to perform due to the large dimension of the space of density matrices. This work develops machine learning algorithms to overcome this difficulty by approximating exact quantum states with neural network parametrisations, specifically Neural Density Operators. As a proof of principle demonstration in a QCD-like theory, the approach is applied to solve the Lindblad master equation in the 1+1D lattice Schwinger Model as an open quantum system. Neural Density Operators enable the study of in-medium dynamics on large lattice volumes, where multiple-string interactions and their effects on string-breaking and recombination phenomena can be studied. Thermal properties of the system at equilibrium can also be probed with these methods by variationally constructing the steady state of the Lindblad master equation. Scaling of this approach with system size is studied, and numerical demonstrations on up to 32 spatial lattice sites and with up to 3 interacting strings are performed.
This work was supported in part by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics, under grant Contract Numbers DE-SC0011090, by Early Career Award DE-SC0021006 and by the Simons Foundation grant 994314 (Simons Collaboration on Confinement and QCD Strings), by he U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, National Quantum Information Science Research Centers, Co-design Center for Quantum Advantage (C2QA) under contract number DE-SC0012704, by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics, InQubator for Quantum Simulation (IQuS) (https://iqus.uw.edu) under Award Number DOE (NP) Award DE-SC0020970 via the program on Quantum Horizons: QIS Research and Innovation for Nuclear Science, by the U.S. National Science Foundation under Cooperative Agreement PHY-2019786 (The NSF AI Institute for Artificial Intelligence and Fundamental Interactions, http://iaifi.org/). The authors acknowledge the MIT SuperCloud and Lincoln Laboratory Supercomputing Center [68] for providing HPC resources that have contributed to the research results reported within this paper.
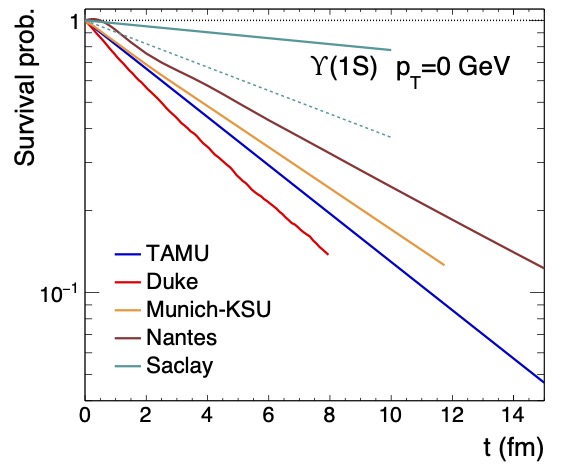
Comparative Study of Quarkonium Transport in Hot QCD Matter
This document summarizes the efforts of the EMMI Rapid Reaction Task Force on “Suppression and (re)generation of quarkonium in heavy-ion collisions at the LHC”, centered around their 2019 and 2022 meetings. It provides a review of existing experimental results and theoretical approaches, including lattice QCD calculations and semiclassical and quantum approaches for the dynamical evolution of quarkonia in the quark-gluon plasma as probed in high-energy heavy-ion collisions. The key ingredients of the transport models are itemized to facilitate comparisons of calculated quantities such as reaction rates, binding energies, and nuclear modification factors. A diagnostic assessment of the various results is attempted and coupled with an outlook for the future.
This work was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) through the CRC-TR 211 ’Strong-interaction matter under extreme conditions’– project number 315477589 – TRR 211; by the Xunta de Galicia (Centro singular de investigacion de Galicia accreditation 2019-2022), the European Union ERDF, the “Maria de Maeztu” Units of Excellence program under projects CEX2020-001035-M and CEX2019-000918-M, the Spanish Research State Agency under projects PID2020-119632GB-I00 and PID2019-105614GB- C21, and the European Research Council under project ERC-2018-ADG-835105 YoctoLHC; by the Generalitat de Catalunya under grant 2021-SGR-249, by U.S. Department of Energy award No. DE-SC0013470; by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics through Contract No. DE-SC0012704; by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics, InQubator for Quantum Simulation (IQuS) under Award Number DE-SC0020970 via the program on Quantum Horizons: QIS Research and Innovation for Nuclear Science; by the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS) and R ́egion Pays de la Loire and acknowledges the support of Narodowe Centrum Nauki under grant no. 2019/34/E/ST2/00186, by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No 824093 (STRONG-2020), by the U.S. Department of Energy Award No. DE-SC0019095 and is grateful for the support and hospitality of the Fermilab theory group; by the U.S. National Science Foundation under grant nos. PHY-1913286 and PHY-2209335; by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics through the Topical Collaboration in Nuclear Theory on Heavy-Flavor Theory (HEFTY) for QCD Matter under award no. DE-SC0023547.
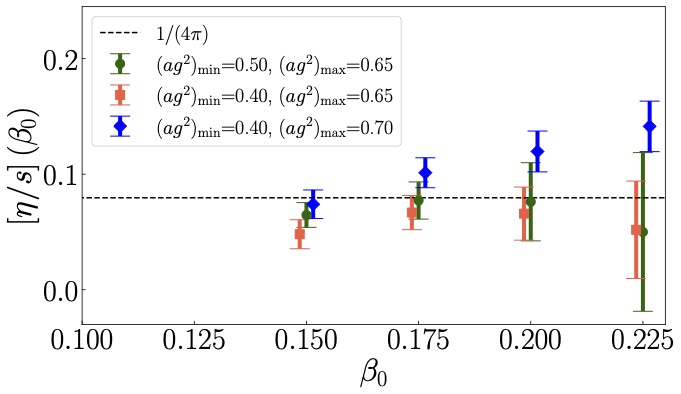
Classical and Quantum Computing of Shear Viscosity for 2+1D SU(2) Gauge Theory
We perform a nonperturbative calculation of the shear viscosity for 2+1-dimensional SU(2) gauge theory by using the lattice Hamiltonian formulation. The retarded Green’s function of the stress-energy tensor is calculated from real time evolution via exact diagonalization of the lattice Hamiltonian with a local Hilbert space truncation and the shear viscosity is obtained via the Kubo formula. When taking the continuum limit, we account for the renormalization group flow of the coupling but no additional operator renormalization. We find the ratio of the shear viscosity and the entropy density eta/s is consistent with a well-known holographic result 1/(4 pi) at several temperatures on a 4×4 hexagonal lattice with the local electric representation truncated at j_max=1/2. We also find the ratio of the spectral function and frequency rho^(xy)(omega)/omega exhibits a peak structure when the frequency is small. Both exact diagonalization method and simple matrix product state classical simulation method beyond j_max=1/2 on bigger lattices require exponentially growing resources. So we develop a quantum computing method to calculate the retarded Green’s function and analyze various systematics of the calculation including j_max truncation and finite size effects and Trotter errors. We test our quantum circuit on both the Quantinuum emulator and the IBM simulator for a small lattice and obtain results consistent with the classical computing ones.
This work is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics, InQubator for Quantum Simulation (IQuS) (https://iqus.uw.edu) under Award Number DOE (NP) Award DE-SC0020970 via the program on Quantum Horizons: QIS Research and Innovation for Nuclear Science. A.C. acknowledges support from the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science under contract DE-AC02-05CH11231, partially through Quantum Information Science Enabled Discovery (QuantISED) for High Energy Physics (KA2401032). This research used resources of the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, which is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE- AC05-00OR22725. We acknowledge the use of Quantinum and IBM Quantum services for this work.
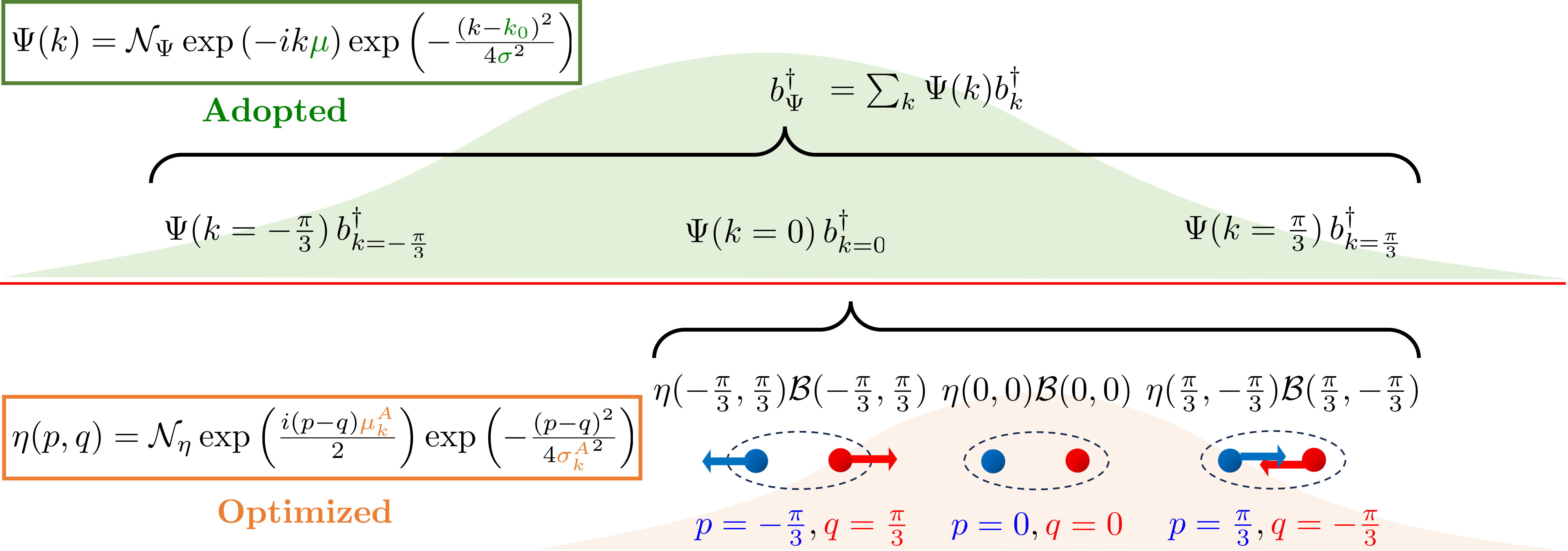
Scattering wave packets of hadrons in gauge theories: Preparation on a quantum computer
Quantum simulation holds promise of enabling a complete description of high-energy scattering processes rooted in gauge theories of the Standard Model. A first step in such simulations is preparation of interacting hadronic wave packets. To create the wave packets, one typically resorts to adiabatic evolution to bridge between wave packets in the free theory and those in the interacting theory, rendering the simulation resource intensive. In this work, we construct a wave-packet creation operator directly in the interacting theory to circumvent adiabatic evolution, taking advantage of resource-efficient schemes for ground-state preparation, such as variational quantum eigensolvers. By means of an ansatz for bound mesonic excitations in confining gauge theories, which is subsequently optimized using classical or quantum methods, we show that interacting mesonic wave packets can be created efficiently and accurately using digital quantum algorithms that we develop. Specifically, we obtain high-fidelity mesonic wave packets in the Z_2 and U(1) lattice gauge theories coupled to fermionic matter in 1+1 dimensions. Our method is applicable to both perturbative and non-perturbative regimes of couplings. The wave-packet creation circuit for the case of the Z_2 lattice gauge theory is built and implemented on the Quantinuum H1-1 trapped-ion quantum computer using 13 qubits and over 300 entangling gates. The fidelities agree well with classical benchmark calculations after employing a simple symmetry-based noise-mitigation technique. This work serves as a step toward quantum computing scattering processes in quantum chromodynamics.
This work is supported, in part, by the DOE QuantISED program through the theory consortium “Intersections of QIS and Theoretical Particle Physics” at Fermilab (Fermilab subcontract no. 666484)
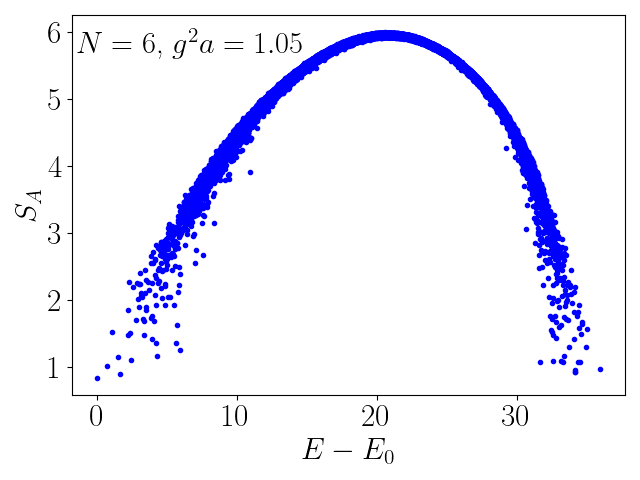
Entanglement Entropy of 2+1-Dimensional SU(2) Lattice Gauge Theory on Plaquette Chains
We study the entanglement entropy of Hamiltonian SU(2) lattice gauge theory in 2+1 dimensions on linear plaquette chains and show that the entanglement entropies of both ground and excited states follow Page curves. The transition of the subsystem size dependence of the entanglement entropy from the area law for the ground state to the volume law for highly excited states is found to be described by a universal crossover function. Quantum many-body scars in the middle of the spectrum, which are present in the electric flux truncated Hilbert space, where the gauge theory can be mapped onto an Ising model, disappear when higher electric field representations are included in the Hilbert space basis. This suggests the continuum 2+1-dimensional SU(2) gauge theory is a “fast” scrambler.
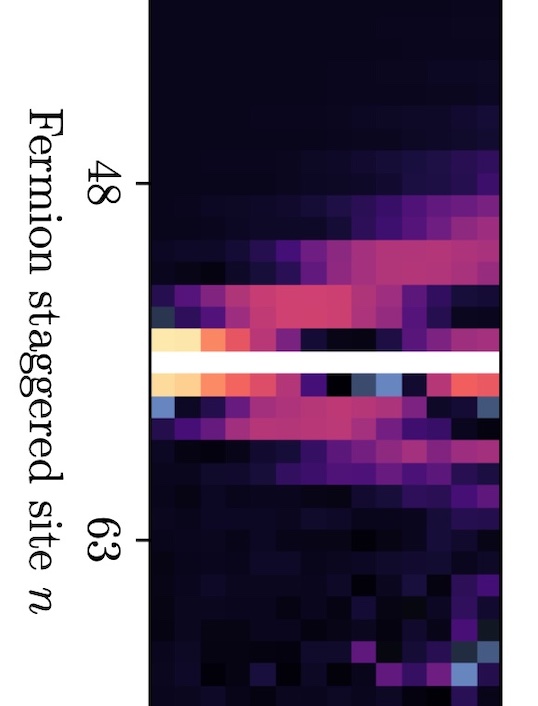
Quantum Simulations of Hadron Dynamics in the Schwinger Model using 112 Qubits
Hadron wavepackets are prepared and time evolved in the Schwinger model using 112 qubits of IBM’s 133-qubit Heron quantum computer ibm_torino. The initialization of the hadron wavepacket is performed in two steps. First, the vacuum is prepared across the whole lattice using the recently developed SC-ADAPT-VQE algorithm and workflow. SC-ADAPT-VQE is then extended to the preparation of localized states, and used to establish a hadron wavepacket on top of the vacuum. This is done by adaptively constructing low-depth circuits that maximize the overlap with an adiabatically prepared hadron wavepacket. Due to the localized nature of the wavepacket, these circuits can be determined on a sequence of small lattices using classical computers, and then robustly scaled to prepare wavepackets on large lattices for simulations using quantum computers. Time evolution is implemented with a second-order Trotterization. To reduce both the required qubit connectivity and circuit depth, an approximate quasi-local interaction is introduced. This approximation is made possible by the emergence of confinement at long distances, and converges exponentially with increasing distance of the interactions. Using multiple error-mitigation strategies, up to 14 Trotter steps of time evolution are performed, employing 13,858 two-qubit gates (with a CNOT depth of 370). The propagation of hadrons is clearly identified, with results that compare favorably with Matrix Product State simulations. Prospectsfor a near-term quantum advantage in simulations of hadron scattering are discussed.
This work was supported, in part, by the U.S. Department of Energy grant DE-FG02-97ER-41014 (Farrell), by U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics, InQubator for Quantum Simulation (IQuS)14 under Award Number DOE (NP) Award DE-SC0020970 via the program on Quantum Horizons: QIS Research and Innovation for Nuclear Science (Ciavarella, Farrell, Savage), the Quantum Science Center (QSC) which is a National Quantum Information Science Research Center of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) (Illa), and by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Science under contract DE-AC02-05CH11231, through Quantum Information Science Enabled Discovery (QuantISED) for High Energy Physics (KA2401032) (Ciavarella). This work is also supported, in part, through the Department of Physics and the College of Arts and Sciences at the University of Washington. This research used resources of the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF), which is a DOE Office of Science User Facility supported under Contract DE-AC05-00OR22725. We acknowledge the use of IBM Quantum services for this work. The views expressed are those of the authors, and do not reflect the official policy or position of IBM or the IBM Quantum team.
Recent Developments in Quarkonium as an Open Quantum System in Quark-Gluon Plasma
We review recent progress in understanding quarkonium dynamics inside the quark-gluon plasma as an open quantum system with a focus on the definition and nonperturbative calculations of relevant transport coefficients and generalized gluon distributions.
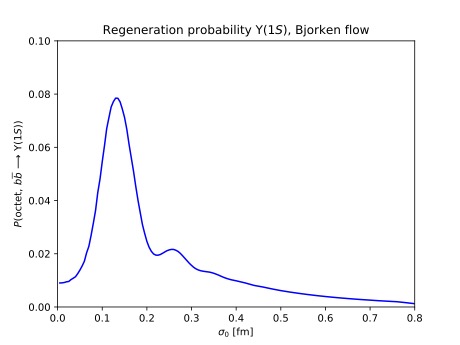
Quarkonium transport in weakly and strongly coupled plasmas
We report on progress in the nonperturbative understanding of quarkonium dynamics inside a thermal plasma. The time evolution of small-size quarkonium is governed by two-point correlation functions of chromoelectric fields dressed with an adjoint Wilson line, known in this context as generalized gluon distributions (GGDs). The GGDs have been calculated in both weakly and strongly coupled plasmas by using perturbative and holographic methods. Strikingly, the results of our calculations for a strongly coupled plasma indicate that the quarkonium dissociation and recombination rates vanish in the transport descriptions that assume quarkonium undergoes Markovian dynamics. However, this does not imply that the dynamics is trivial. As a starting point to explore the phenomenological consequences of the result at strong coupling, we show a calculation of the $\Upsilon(1S)$ formation probability in time-dependent perturbation theory. This is a first step towards the development of a transport formalism that includes non-Markovian effects, which, depending on how close the as of yet undetermined nonperturbative QCD result of the GGDs is to the strongly coupled $\mathcal{N}=4$ SYM result, could very well dominate over the Markovian ones in quark-gluon plasma produced at RHIC and the LHC.
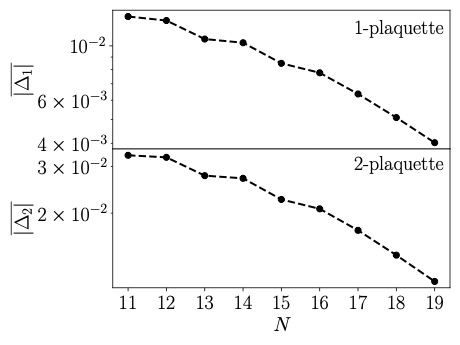
Testing Eigenstate Thermalization Hypothesis for Non-Abelian Gauge Theories
We report on progress in full quantum understanding of thermalization in non-Abelian gauge theories. Specifically, we test the eigenstate thermalization hypothesis for (2+1)-dimensional SU(2) lattice gauge theory.


